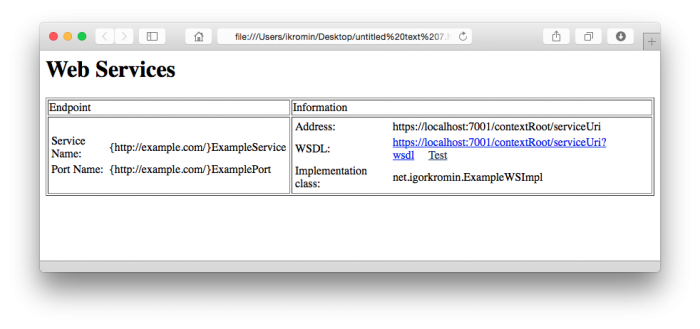
Making this change is almost trivial. Simply change the transport-guarantee element of your web.xml file. There are three possible values for this, NONE, INTEGRAL and CONFIDENTIAL. Both of the latter force SSL.
Here's more information from WebLogic documentation:
Specifies data security requirements for communications between the client and the server.
Range of values:
NONE—The application does not require any transport guarantees.
INTEGRAL—The application requires that the data be sent between the client and server in such a way that it cannot be changed in transit.
CONFIDENTIAL—The application requires that data be transmitted so as to prevent other entities from observing the contents of the transmission.
WebLogic Server establishes a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connection when the user is authenticated using the INTEGRAL or CONFIDENTIAL transport guarantee.
Range of values:
NONE—The application does not require any transport guarantees.
INTEGRAL—The application requires that the data be sent between the client and server in such a way that it cannot be changed in transit.
CONFIDENTIAL—The application requires that data be transmitted so as to prevent other entities from observing the contents of the transmission.
WebLogic Server establishes a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connection when the user is authenticated using the INTEGRAL or CONFIDENTIAL transport guarantee.
In my case, I change the web.xml to something like this:
web.xml
...
<user-data-constraint>
<description>The application requires that the data be sent between the client and server in such a way that it cannot be changed in transit.</description>
<transport-guarantee>INTEGRAL</transport-guarantee>
</user-data-constraint>
...
Now even when using basic authentication, since SSL is used, the username and password will be encrypted. It is still possible to send a request to the non-SSL URL for the web service however. In this case, WebLogic will respond with the testing page instead of forwarding the request to the web service.
-i